News 1: ‘On track to attract $100 bn FDI this year’
Background:
- India is on track to attract $100 billion foreign direct investment (FDI) in the current fiscal on account of economic reforms and ease of doing business, the Centre said on Saturday.
- In 2021-22, India received the “highest ever” foreign inflows of $83.6 billion. “This FDI has come from 101 countries, and invested across 31 Union Territories and States and 57 sectors in the country,” the Commerce and Industry Ministry said in a statement.
Foreign Direct Investment:

- Foreign direct investment (FDI) is when a company takes controlling ownership in a business entity in another country.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a category of cross-border investment in which an investor resident in one economy establishes a lasting interest in and a significant degree of influence over an enterprise resident in another economy.
- Ownership of 10 percent or more of the voting power in an enterprise in one economy by an investor in another economy is evidence of such a relationship.
Benefits of FDI:
- FDI is a key element in international economic integration because it creates stable and long-lasting links between economies.
- FDI is an important channel for the transfer of technology between countries, promotes international trade through access to foreign markets, and can be an important vehicle for economic development.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) has proved to be resilient during financial crises. For instance, in East Asian countries, such investment was remarkably stable during the global financial crises of 1997-98.
- FDI is a key driver in economic growth and a significant non-debt financial resource of Indian economy.
- FDI allows the transfer of technology—particularly in the form of new varieties of capital inputs—that cannot be achieved through financial investments or trade in goods and services.
- FDI can also promote competition in the domestic input market.
- Recipients of FDI often gain employee training in the course of operating the new businesses, which contributes to human capital development in the host country.
- Profits generated by FDI contribute to corporate tax revenues in the host country.
FDI in India:
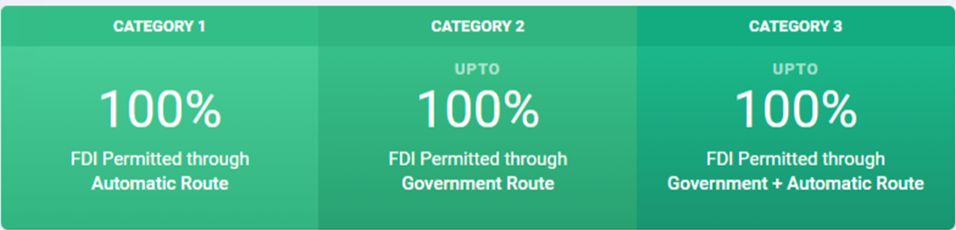
Automatic Route
- Under the Automatic Route, the non-resident investor or the Indian company does not require any approval from Government of India for the investment.
Government Route
- Under the Government Route, prior to investment, approval from the Government of India is required. Proposals for foreign direct investment under Government route, are considered by respective Administrative Ministry/ Department.
Singapore (27.01%), USA (17.94%), Mauritius (15.98%), Netherland (7.86%) and Switzerland (7.31%) emerge as top 5 countries for FDI equity inflows into India FY 2021-22.
Top 5 sectors receiving highest FDI Equity Inflow during FY 2021-22 are Computer Software & Hardware (24.60%), Services Sector (Fin., Banking, Insurance, Non Fin/Business, Outsourcing, R&D, Courier, Tech. Testing and Analysis, Other) (12.13%), Automobile Industry (11.89%), Trading 7.72% and Construction (Infrastructure) Activities (5.52%).
Top 5 States receiving highest FDI Equity Inflow during FY 2021-22 are Karnataka (37.55%), Maharashtra (26.26%), Delhi (13.93%), Tamil Nadu (5.10%) and Haryana (4.76%)
India’s FDI inflows have increased 20 times from 2000-01 to 2021-22. According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), India’s cumulative FDI inflow stood at US$ 847.40 billion between April 2000-March 2022; this was mainly due to the government’s efforts to improve the ease of doing business and relax FDI norms.
News 2: Operation Megh Chakra
Background:
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) on Saturday conducted searches at 59 locations across 20 States and one Union Territory, as part of a pan-India drive against the circulation and sharing of child sexual abuse material.
Operation Megh Chakra:
- The CBI has registered two cases alleging that a large number of Indian nationals were involved in the online circulation, downloading and transmission of such material using cloud-based storage.
- The searches were carried out in Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Goa, Karnataka, Telangana and Tamil Nadu. The agency seized electronic devices belonging to the suspects.
- A preliminary scrutiny of the devices using cyberforensic tools allegedly revealed that a huge quantity of child pornography material was stored in them. “The suspects are being questioned to identify the victims and the abusers,” said an official, adding that the operation was one of the CBI-led global operations in recent times for a prompt response to online child sexual exploitation cases with international linkages.
- The official said the operation sought to collate information from various law enforcement agencies in India, engage with the relevant law enforcement agencies globally and coordinate closely through the Interpol channels on the issue.
Child security in cyberspace:
- Section 67B of the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000 provides stringent punishment for publishing, transmitting or viewing child sexual abuse material online.
- The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 empower the users of Intermediaries and makes the social media platforms accountable for their safety. The Rules also require Significant Social Media Intermediary (SSMI) to endeavor to deploy technology-based measures to proactively identify child sexual abuse material.
- Government periodically blocks the websites containing extreme child sexual abuse material (CSAM) based on INTERPOL’s “worst of list” received through Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), the national nodal agency for Interpol in India.
- Government has issued an order to concerned Internet Service Providers (ISPs) ordering them to implement Internet Watch Foundation (IWF), UK or Project Arachnid, Canada list of CSAM websites/webpages on a dynamic basis and block access to such child pornography webpages/websites.
- Meity through a program, namely, Information Security Education & Awareness (ISEA), has been creating awareness among users including women and children highlighting the importance of digital safety while using Internet.
- Further, Section-14 of the Protection of Children from Sexual Offence (POCSO) Act provides Punishment for using child for pornographic purposes.
News 3: Odisha offering cash incentive to PVTGs for marrying after 18
Background:
- Keeping the rampant child marriages among the Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) of Odisha in mind, the State government is providing an incentive of ₹20,000 for late marriage.
- Offered by the Odisha PVTG Empowerment and Livelihoods Improvement Programme (OPELIP), a special programme designed to improve living conditions and reduce poverty among the PVTGs, the money is given to the couples marrying after the age of 18 years.
Impact of child marriage:
- It negatively influences children’s rights to education, health and protection. These consequences impact not just the girl directly, but also her family and community.
- A girl who is married as a child is more likely to be out of school and not earn money and contribute to the community. She is more likely to experience domestic violence and become infected with HIV/AIDS. She is more likely to have children when she is still a child. There are more chances of her dying due to complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
- Child marriage violates children’s rights and places them at high risk of violence, exploitation, and abuse. Child marriage affects both girls and boys, but it affects girls disproportionately.
- Asper UNICEF, While the prevalence of girls getting married before age 18 has declined from 47 per cent to 27 per cent between 2005-2006 and 2015-2016 it is still too high.
- Child marriage negatively affects the Indian economy and can lead to an intergenerational cycle of poverty.
- Sustainable Development Goal – child marriage is included in Goal 5 “Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls” under Target 5.3 “Eliminate all harmful practices, such as child, early and forced marriage and female genital mutilation”
PVTG (Particularly vulnerable tribal Groups):
Government of India follows the following criteria for identification of PVTGs.
- Pre-agricultural level of technology
- Low level of literacy
- Economic backwardness
- A declining or stagnant population.
Accordingly, 75 PTVGs have been identified in the country. Odisha accounts for highest number of PVTGs in India.
In 1973, the Dhebar Commission created Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs) as a separate category, who are less developed among the tribal groups. In 2006, the Government of India renamed the PTGs as Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
PVTGs have some basic characteristics -they are mostly homogenous, with a small population, relatively physically isolated, social institutes cast in a simple Mould, absence of written language, relatively simple technology and a slower rate of change etc.
News 4: Election Commission to push for internal democracy in parties
Background:
- After taking action against registered unrecognised political parties (RUPPs) for failing to comply with norms, the Election Commission is likely to take up the issue of internal democracy within parties next, according to EC sources.
- Though the Representation of the People Act does not mandate internal elections, the EC’s guidelines for parties applying for registration under the Act state that the applicant should submit a copy of the party constitution.
Election Commission of India:
Established: 25 January 1950 (Celebrated as National Voters Day)
Type: Autonomous Constitutional body
Responsibilities:
- The Election Commission of India is responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India.
- Article 324 of the Constitution provides that the power of superintendence, direction, and control of elections to parliament, state legislatures, the office of the president of India, and the office of vice-president of India shall be vested in the election commission
Appointment and tenure:
- The President appoints Chief Election Commissioner and Election Commissioners. They have tenure of six years, or up to the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- They enjoy the same status and receive salary and perks as available to Judges of the Supreme Court of India. The Chief Election Commissioner can be removed from office only through impeachment by Parliament.
Voting:
- The democratic system in India is based on the principle of universal adult suffrage; that any citizen over the age of 18 can vote in an election (before 1989 the age limit was 21). The right to vote is irrespective of caste, creed, religion or gender.
- Those who are deemed unsound of mind, and people convicted of certain criminal offences are not allowed to vote. There has been a general increase in the number of people voting in Indian election.
Who can stand for election?
- Any Indian citizen who is registered as a voter is otherwise not disqualified under the Law and is over 25 years of age is allowed to contest elections to the Lok Sabha or State Legislative Assemblies. For the Rajya Sabha the age limit is 30 years. Candidates for Vidhan Sabha should be residents of the same state from which they wish to contest.
- Every candidate has to make deposit of Rs. 25,000/- for Lok Sabha election and Rs. 10,000/- for Rajya Sabha or Vidhan Sabha elections, except for candidates from the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes who pay half of these amounts. The deposit is returned if the candidate receives more than one-sixth of the total number of valid votes polled in the constituency.
- Nominations must be supported at least by one registered elector of the constituency, in the case of a candidate sponsored by a recognised Party and by ten registered electors from the constituency in case of other candidates.
News 5: ‘Non-oil exports to UAE up 14% after trade deal; surge 3% globally’
Background:
- India’s non-oil exports to the UAE have grown 14% between June and August, the Commerce and Industry Ministry said on Sunday, attributing the uptick to the bilateral deal between the two nations that came into effect this May.
India – UAE relations:
Trading and commerce relations:
- The trade, which was dominated by traditional items such as dates, pearl and fishes, underwent a sharp change after the discovery of oil in UAE (oil exports begun from Abu Dhabi in 1962). With the emergence of UAE as a unified entity in 1971, exports from India started growing gradually over the years.
- Both sides are striving to further strengthen these ties for mutual benefits. India-UAE trade, valued at US$ 180 million per annum in the 1970s, is today US$ 59 billion making UAE, India’s third largest trading partner for the year 2019-20 after China and US.
- Moreover, UAE is the second largest export destination of India (after US) with an amount of nearly US$ 29 billion for the year 2019-20. For UAE, India is the second largest trading partner for the year 2019 with an amount of around US$ 41.43 billion (non-oil trade).
- The sharpest jump in Indian exports to UAE was seen in sugar (up 237%), cereals (161%), vegetables (82%), inorganic chemicals (74%) and electrical machinery and equipment (67%).
- The Ministry said it expects Indian exports to increase further in the coming months with increasing use of the India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) by exporters and a series of trade promotion events planned in the UAE.
- Gems & Jewellery sector contributes a substantial portion of India’s exports to the UAE and is a sector that is expected to benefit significantly from the tariff concessions obtained for Indian products under the India-UAE CEPA.
- Overall, India will benefit from preferential market access provided by the UAE on over 97 % of its tariff lines which account for 99% of Indian exports to the UAE in value terms particularly from labour-intensive sectors such as Gems and Jewellery, Textiles, leather, footwear, sports goods, plastics, furniture, agricultural and wood products, engineering products, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and Automobiles.
- As regards trade in services, Indian service providers will have enhanced access to around 111 sub-sectors from the 11 broad service sectors.
- CEPA is expected to increase the total value of bilateral trade in goods to over US$100 billion and trade in services to over US$ 15 billion within five years.
News 6: Flex fuel: Part of plan to cut crude imports, but policy support key
Background:
- India’s first ‘flex fuel’ car, a Toyota sedan that can run on one or multiple fuel types and developed as part of a new pilot aimed at deleveraging the country’s dependence on imported fossil fuels for transportation, is set for an unveiling later this month.
Flex fuel technology:
- A flex fuel, or flexible fuel, vehicle has an internal combustion engine (ICE), but unlike a regular petrol or diesel vehicle, this can run on more than one type of fuel, or even a mixture of fuels. The most common versions use a blend of petrol and ethanol or methanol, but these engines are also equipped to run on 100 per cent petrol or ethanol as well.
- This is made possible by equipping the engine with a fuel mix sensor and an engine control module (ECM) programming that senses and automatically adjusts for any ratio of designated fuels.
- Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari said the push to car makers to adopt flexible engines is part of a broader strategy to cut down on the country’s dependence on imported crude in the medium-to-long run.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- The use of ethanol blending sharply lowers harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide, sulphur, and carbon and nitrogen oxides.
- Blending will help cut back on oil imports for fueling vehicles.
- Many flex fuel vehicles have improved acceleration performance when operating on higher ethanol blends
Cons:
- A flex fuel car typically takes a small hit on fuel efficiency when using ethanol for motive power, ranging from between 4 per cent and 8 per cent.
- A major problem with ethanol blending is that crops such as sugarcane are usually very water-intensive. A NITI Aayog report suggested that in 2019-20, of the total ethanol produced in the country, over 90 per cent came from sugarcane alone.
- Plus, sugarcane is a politically important crop in states such as Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh, and there is a perceived political angle to the ethanol/methanol blending push.
Ethanol blending in India:
- Currently, around 9.5 per cent ethanol blending with petrol has been achieved in fuel dispensed in pumps in most metros and it is likely that the targeted 10 per cent ethanol blending will be achieved by November 2022.
- But this is slated for a major bump up, with the government’s 2025 target of 20 per cent blending of ethanol in petrol envisaged in its National Biofuel Policy 2018.
National Biofuel Policy 2018:
- The Goal of the Policy is to enable availability of biofuels in the market thereby increasing its blending percentage. Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas (MoP&NG) has notified that Oil Companies shall sell Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) with percentage of ethanol up to twenty per cent throughout the country from 01st April 2023.
- Blending of ethanol in Petrol will gradually be increased in the coming years. A target of 20% blending of ethanol in petrol is proposed by Ethanol Supply Year (ESY) 2025-26.
- An indicative target of 5% blending of biodiesel in diesel /direct sale of biodiesel is proposed by 2030. This goal is to be achieved by (a) reinforcing ongoing ethanol/biodiesel supplies through increasing domestic production (b) setting up Second Generation (2G) bio refineries (c) development of new feedstock for biofuels (d) development of new technologies for conversion to biofuels (e) creating suitable environment for biofuels and its integration with the main fuels
Salient features:
The Policy categorises biofuels as “Basic Biofuels” viz.
- First Generation (1G) bioethanol & biodiesel
- “Advanced Biofuels” – Second Generation (2G) ethanol,
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) to drop-in fuels,
- Third Generation (3G) biofuels, bio-CNG etc. to enable extension of appropriate financial and fiscal incentives under each category.
The Policy expands the scope of raw material for ethanol production by allowing use of Sugarcane Juice, Sugar containing materials like Sugar Beet, Sweet Sorghum, Starch containing materials like Corn, Cassava, Damaged food grains like wheat, broken rice, Rotten Potatoes, unfit for human consumption for ethanol production.
Farmers are at a risk of not getting appropriate price for their produce during the surplus production phase. Taking this into account, the Policy allows use of surplus food grains for production of ethanol for blending with petrol with the approval of National Biofuel Coordination Committee.
With a thrust on Advanced Biofuels, the Policy indicates a viability gap funding scheme for 2G ethanol Bio refineries of Rs.5000 crore in 6 years in addition to additional tax incentives, higher purchase price as compared to 1G biofuels.
The Policy encourages setting up of supply chain mechanisms for biodiesel production from non-edible oilseeds, Used Cooking Oil, short gestation crops.
Roles and responsibilities of all the concerned Ministries/Departments with respect to biofuels has been captured in the Policy document to synergise efforts.
Expected benefits:
- Reduce Import Dependency: One crore lit of E10 saves Rs.28 crore of forex at current rates. The ethanol supply year 2017-18 is likely to see a supply of around 150 crore litres of ethanol which will result in savings of over Rs.4000 crore of forex.
- Cleaner Environment: One crore lit of E-10 saves around 20,000 ton of CO2 emissions. For the ethanol supply year 2017-18, there will be lesser emissions of CO2 to the tune of 30 lakh ton. By reducing crop burning & conversion of agricultural residues/wastes to biofuels there will be further reduction in Green House Gas emissions.
- Health benefits: Prolonged reuse of Cooking Oil for preparing food, particularly in deep-frying is a potential health hazard and can lead to many diseases. Used Cooking Oil is a potential feedstock for biodiesel and its use for making biodiesel will prevent diversion of used cooking oil in the food industry.
- MSW Management: It is estimated that, annually 62 MMT of Municipal Solid Waste gets generated in India. There are technologies available which can convert waste/plastic, MSW to drop in fuels. One ton of such waste has the potential to provide around 20% of drop in fuels.
- Infrastructural Investment in Rural Areas: It is estimated that, one 100klpd bio refinery will require around Rs.800 crore capital investment. At present Oil Marketing Companies are in the process of setting up twelve 2G bio refineries with an investment of around Rs.10,000 crore. Further addition of 2G bio refineries across the Country will spur infrastructural investment in the rural areas.
- Employment Generation: One 100klpd 2G bio refinery can contribute 1200 jobs in Plant Operations, Village Level Entrepreneurs and Supply Chain Management.
- Additional Income to Farmers: By adopting 2G technologies, agricultural residues/waste which otherwise are burnt by the farmers can be converted to ethanol and can fetch a price for these waste if a market is developed for the same. Also, farmers are at a risk of not getting appropriate price for their produce during the surplus production phase. Thus conversion of surplus grains and agricultural biomass can help in price stabilization.
Other important news
Masai tribe:
- The Maasai tribe are an indigenous ethnic group in Africa of semi-nomadic people settled in Kenya and northern Tanzania.
- Cheetahs require large expanses of land that can support prey and suitable cover to thrive. One such habitat is the famed Masai Mara, a large game reserve in Kenya, named in honour of the Masai tribe.

Mars rover Perseverance collects four rock samples:
Since July, NASA’s Perseverance rover has drilled and collected four slim cores of sedimentary rock, formed in what was once a river delta on Mars. They are the first of this type of rock to be gathered on another world — and scientists are excited because at least two of the cores probably contain organic compounds, which, on Earth, are often associated with living things. If all goes well, the samples will be the first-ever returned from Mars.
Perseverance rover:
- Main Job: Seek signs of ancient life and collect samples of rock and regolith (broken rock and soil) for possible return to Earth.
- Mars 2020 is a Mars rover mission forming part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program that includes the rover Perseverance, the small robotic, coaxial helicopter Ingenuity, and associated delivery vehicles.
Kaziranga National Park:
- Kaziranga National Park is a national park in the Golaghat and Nagaon districts of the state of Assam, India. The park, which hosts two-thirds of the world’s great one-horned rhinoceroses, is a World Heritage Site.
- Kaziranga is a UNESCO world heritage site, a tiger reserve, important bird area as declared by BirdLife International and is located on the edge of Eastern Himalaya biodiversity hotspot.
- It hosts the iconic Greater one-horned rhinoceros, the park is the breeding ground of elephants, wild water buffalo, tiger and swamp deer.
Dal Lake:
- Dal is a lake is in Srinagar (Dal Lake is a misnomer as Dal in Kashmiri means lake), the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir. The urban lake is integral to tourism and recreation in Kashmir and is named the “Jewel in the crown of Kashmir” or “Srinagar’s Jewel” or “Lake of flowers”.
- The lake is also an important source for commercial operations in fishing and water plant harvesting.
- At present, the Dal and the Mughal gardens on its periphery are undergoing intensive restoration measures to fully address the serious eutrophication problems experienced by the lake.


