UPSC/STATE PSC
Curated by Experts For Civil Service Aspirants
The Hindu & Indian Express
News 1: ‘Adopt a TB patient’ drive mitras
Background:
- The Union Health Ministry’s “adopt a TB-patient” (Ni-kshay Mitra) initiative, and it was to fill the critical “community” element into India’s fight towards eliminating TB by 2025 under the Pradhan Mantri TB-Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan.
Burden of TB:
- India has the world’s highest tuberculosis (TB) burden, with 26 lakh people contracting the disease and approximately four lakh people dying from it every year.
- The economic burden of TB in terms of the loss of lives, income and workdays is also substantial.
- TB usually affects the most economically productive age group of society resulting in a significant loss of working days.
Ni-kshay Mitra:
- The support provided to the patient under this initiative is in addition to the free diagnostics, free drugs and the Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana provided by the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP) to all the patients notified from both the public and the private sector.
Donors:
- Cooperative societies, corporates, elected representatives, individuals, institutions, non-governmental organizations, political parties and partners willing to adopt the health facilities (for individual donor) and urban wards, blocks, districts and States for accelerating the response against TB to complement the government’s efforts.
- Some donors would provide additional support to all the on-treatment TB patients who had given consent for support, in the selected health facilities, blocks, urban wards, districts and States. Others have to choose the entire geographical unit (blocks, urban wards, districts and States). The minimum period of commitment for providing the support to the TB patient will be one year.
News 2: ‘Mastermind’ behind Chinese shell firms held
Background:
- The Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO) late on Saturday arrested a person said to be the mastermind behind a slew of Chinese shell companies operating in the country, from a remote part of Bihar while he was attempting to cross the border through the land route.
Serious Fraud Investigation Office:
- Established: 2003 as per Companies Act, 2013
- Headquarter: New Delhi
- Ministry: Ministry of Corporate Affairs
- Type: Statutory organization
- Objective: It is involved in detecting and prosecuting or recommending for prosecution white-collar crimes/frauds. The SFIO is mandated to conduct Multi-disciplinary investigations of major corporate frauds
Shell companies:
- A shell corporation is a corporation without active business operations or significant assets. These types of corporations are not all necessarily illegal, but they are sometimes used illegitimately, such as to disguise business ownership from law enforcement or the public.
News 3: Project 17A Taragiri
Background:
- Taragiri, the third stealth frigate of the Project 17A, was launched on Sunday by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd. (MDL).
Taragiri:
- Indigenously designed Taragiri will have state-of-the-art weapons, sensors, an advanced action information system, an integrated platform management system, world class modular living spaces, a sophisticated power distribution system and a host of other advanced features.
- It will be fitted with a supersonic surface-to-surface missile system and the ship’s air defence capability is designed to counter the threat of the enemy aircraft and the anti-ship cruise missiles would revolve around the vertical launch and long-range surface to air missile system.
Project 17A:
- The programme involves the development of 7 advanced guided missile frigates, of which 4 will be built by Mazagaon Dock Shipbuilders and the remaining three ships by GRSE.
- The Nilgiri-class stealth frigates, are also known as Project 17A frigates and it is a follow-on of the Project 17 Shivalik –class frigates.
- The names of ships are based on the names of hill ranges in India i.e., INS Nilgiri, INS Himgiri, INS Udaygiri, INS Dunagiri, INS Taragiri, INS Vindhyagiri, INS Mahendragiri
Ships of Project 17A:
- It will generate employment opportunities for more than 2000 companies and MSMEs in the country.
- Approximately, 80% of the materials and equipment are being sourced from domestic vendors, thus giving a fillip to domestic manufacturers.
News 4: India stays out of ‘trade pillar’ at Indo-Pacific meet
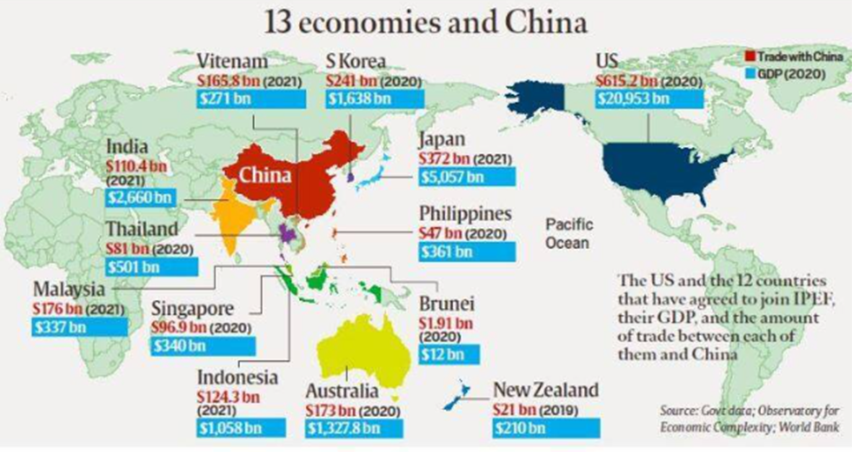
Background:
- India stayed out of the joint declaration on the trade pillar of the U.S.-led Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF) ministerial meet in Los Angeles, with Union Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal citing concerns over possible discrimination against developing economies.
- India was the only one of the 14 IPEF countries, which include Southeast Asian countries, Australia, New Zealand, South Korea and Japan, not to join the declaration on trade.
India’s position on IPEF:
- India was “comfortable” with the outcome statements on the other three pillars: supply chains, clean economy (clean energy) and fair economy (tax and anti-corruption).
- India will be staying out of the trade pillar as the “contours of the framework” had not emerged yet, particularly on the kind of commitment each country would have to make on “environment, labour, digital trade and public procurement.
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework
- The development of an Indo-Pacific economic framework that will define the shared objectives around trade facilitation, standards for the digital economy and technology, supply chain resiliency, decarbonization and clean energy, infrastructure, worker standards, and other areas of shared interest.
- Launched: US President Joe Biden launched it in 2022
- Members: Australia, Brunei, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, United States, and Vietnam.
Four pillars:
- Fair and resilient trade
- Supply chain resilience
- Infrastructure, clean energy, and decarbonization
- Tax and anti-corruption
News 5: New adoption rules create confusion

Background:
- Parliament passed the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Amendment Bill, 2021, in July last year, which empowers DMs to give adoption orders. The intent of the amendment was to prevent court-related delays during adoptions because of a large number of pending cases. The amendments came into effect from September 1.
Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA)
- Type: Statutory
- Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Function and Mission: It functions as the nodal body for adoption of Indian children and is mandated to monitor and regulate in-country and inter-country adoptions.
- CARA is designated as the Central Authority to deal with inter-country adoptions in accordance with the provisions of the Hague Convention on Inter-country Adoption, 1993, ratified by Government of India in 2003.
- CARA primarily deals with adoption of orphan, abandoned and surrendered children through its associated /recognized adoption agencies.
News 6: Why Cloudburst forecast still remains elusive in India
Cloudbursts:
- Cloudbursts are violent and voluminous amounts of rain pouring down in a short duration over a small area.
- Cloudburst events are often associated with cumulonimbus clouds that cause thunderstorms and occasionally due to monsoon wind surges and other weather phenomena.
- Cumulonimbus clouds can grow up to 12-15 km in height through the entire troposphere (occasionally up to 21 km) and can hold huge amounts of water.
- According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), 100 mm of rain in an hour is called a cloudburst.
- Usually, cloudbursts occur over a small geographical region of 20 to 30 sq. km.
Occurrence of Cloudbursts:
- In India, cloudbursts often occur during the monsoon season, when the southwesterly monsoon winds bring in copious amounts of moisture inland.
- The moist air that converges over land gets lifted as they encounter the hills. The moist air reaches an altitude and gets saturated, and the water starts condensing out of the air forming clouds.
- An orographic lifting together with a strong moisture convergence can lead to intense cumulonimbus clouds taking in huge volumes of moisture that is dumped during cloudbursts.
Areas affected by cloudbursts:
- Cloudbursts, hence, occur mostly over the rugged terrains over the Himalayas, the Western Ghats, and northeastern hill States of India.
- The heavy spells of rain on the fragile steep slopes trigger landslides, debris flows, and flash floods, causing large-scale destruction and loss of people and property.
Reasons behind difficult detection of cloudbursts:
- The change in monsoon extremes and cloudbursts we see now are in response to the 1-degree Celsius rise in global surface temperature.
- A 1-degree Celsius rise in temperature may correspond to a 7-10% increase in moisture and rainfall.
- The forecasting of rainfall in hilly regions remains challenging due to the uncertainties in the interaction between the moisture convergence and the hilly terrain, the cloud microphysics, and the heating-cooling mechanisms at different atmospheric levels.
- The resolution of the precipitation radars of the satellites can be much smaller than the area of individual cloudburst events, and hence they go undetected.
- Multiple doppler weather radars can be used to monitor moving cloud droplets and help to provide nowcasts (forecasts for the next three hours).
- As radars are expensive it is not practical to deploy them.
Way forward:
- A long-term measure would be mapping the cloudburst-prone regions using automatic rain gauges.
- People who are located in landslide risk areas and whose condition can be further worsened due to cloudbursts, need to be shifted so as to minimize the impacts of disaster.
- Action and policies to protect lives and property from extreme events are needed as the global temperature change doubles.

News 7: Why is the Kushiyara river treaty important?
Kushiyara agreement:
- The flow of the Barak river has changed in such a way that the bulk of the river’s water flows into Kushiyara while the rest goes into Surma.
- The agreement is aimed at addressing part of the problem that the changing nature of the river has posed before Bangladesh as it unleashes floods during the monsoon and goes dry during the winter when demand of water goes up because of a crop cycle in Sylhet.

Why is Kushiyara river water important for Bangladesh?
- Approximately 10,000 hectares of land and millions of people will benefit from the water that will flow through a network of canals in Sylhet benefiting the farmers involved in cultivation of Boro rice and horticulture crops.
- India initially objected to construction of Rahimpur canal as it interfered with border security but India has now withdrawn this objection.
- The Kushiyara agreement did not require a nod from any of the States like Assam from which the Barak emerges and branches into Kushiyara and Surma.
News 8: India-Saudi ties promise shared growth, security, stability, says Jaishankar
India and Saudi Arabia ties:
- Saudi Arabia is India’s fourth-largest trading partner.
- More than 18 per cent of India’s crude oil imports are sourced from Saudi Arabia.
- The 2.2-million-strong Indian community is the largest expatriate community in Saudi Arabia.
Gulf Cooperation Council:
- It is a regional, intergovernmental, political, and economic union.
- Members: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE
- Headquarters: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
News 9: Supreme Court to take up CAA challenge
Background:
- A three-judge Bench of the Supreme Court led by Chief Justice of India (CJI) U U Lalit will hear the challenge to the Citizenship (Amendment) Act on Monday.
Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019:
- It seeks to grant citizenship to a class of migrants belonging to Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Jain, Parsi or Christian communities from Afghanistan, Bangladesh or Pakistan.
- The legislation applies to those who were “forced or compelled to seek shelter in India due to persecution on the ground of religion”.
- It aims to protect such people from proceedings of illegal migration.
- The cut-off date for citizenship is December 31, 2014 which means the applicant should have entered India on or before that date.
- Indian citizenship, under present law, is given either to those born in India or if they have resided in the country for a minimum of 11 years.
- Exception: The Bill adds that the provisions on citizenship for illegal migrants will not apply to the tribal areas of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, or Tripura, as included in the Sixth Schedule to the Constitution.
- These tribal areas include Karbi Anglong (in Assam), Garo Hills (in Meghalaya), Chakma District (in Mizoram), and Tripura Tribal Areas District.
- It will also not apply to the areas under the Inner Line” under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873.
Who is an illegal migrant?
- An illegal migrant is a foreigner who: (i) enters the country without valid travel documents, like a passport and visa, or (ii) enters with valid documents, but stays beyond the permitted time period.
- Illegal migrants may be imprisoned or deported under the Foreigners Act, 1946 and the Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920. The 1946 and the 1920 Acts empower the central government to regulate the entry, exit and residence of foreigners within India.
Criticisms against CAA:
- Some critics are of the view that the act is unconstitutional.
- Others are of the view that it violates Article 14 of the Constitution that guarantees that no person shall be denied the right to equality before law or the equal protection of law in the territory of India.
- Granting citizenship on the grounds of religion is seen to be against the secular nature of the Constitution which has been recognised as part of the basic structure that cannot be altered by Parliament
- Fears have risen in North east states as this will increase the number of illegal migrants which might threaten the linguistic and cultural identity of people.
News 10: ‘Discoms’ outstanding dues towards gencos to be eliminated by 2026
Background:
- Outstanding dues of electricity distribution companies (discoms) towards gencos, which remains over Rs 1 lakh crore at any point of time, eill be eliminated in next four years, Union Power Minister RK Singh said.
Reasons for losses:
- Power tariffs are not keeping in line with price rises
- Aggregate technical and commercial losses
- Pilferage
- Gap between average cost per unit and realised revenue
- Forcing discoms to reduce their power purchases and delay payments to power producers
Ujwal Discom Assurance Yojana:
- Launch: 2015
- Ministry: Ministry of Power
- Objective: UDAY provides for the financial turnaround and revival of Power Distribution companies (DISCOMs), and importantly also ensures a sustainable permanent solution to the financial mess that the power distribution.
- The scheme envisages: financial turnaround, Operational improvement, Reduction of cost of generation of power, Development of Renewable energy, and energy efficiency and conservation.
Benefits to participating states:

Impact of the scheme:

News 11: Switching lanes in EV race
Background:
- India’s first indigenously-developed hydrogen fuel cell (HFC) technology bus was unveiled late August, with the fuel cell — which uses hydrogen and air to generate electricity onboard to power the bus — being developed jointly by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and Pune-based automotive software company KPIT Ltd.
- India is finding it difficult to make inroads into the global lithium value chain
Problems of using Lithium batteries:
- Demand for Li-ion batteries from India is projected to grow at CAGR of over 30 per cent by volume up to 2030, translating into over 50,000 tonnes of lithium requirement for the country to manufacture only EV batteries.
- With over 90 per cent of global Lithium production concentrated in Chile, Argentina and Bolivia, alongside Australia and China, and other key inputs such as cobalt and nickel mined in the Congo and Indonesia, India would need to be almost entirely dependent on imports from a small pool of countries to cater to its demand.
India’s early stride towards tapping of hydrogen energy:
- National Hydrogen Mission and a roadmap for using hydrogen as an energy source has been promoted and established in India.
- Proposed end-use sectors include steel and chemicals, the major industry that hydrogen has the potential of transforming is transportation — which contributes a third of all greenhouse gas emissions, and where hydrogen is being viewed as a direct replacement of fossil fuels, with specific advantages over traditional EVs.
Hydrogen:
- The most common element in nature, however, is not found freely.
- Hydrogen exists only when combined with other elements and has to be extracted from naturally occurring compounds like water (which is a combination of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom).
- Although hydrogen is a clean molecule, the process of extracting it is energy intensive. The two most common methods for producing hydrogen are natural gas reforming and electrolysis.
Processes involving production of Hydrogen:
- The thermal processes for hydrogen production typically involve steam reforming, a process in which steam reacts with a hydrocarbon fuel to produce hydrogen and accounts for about 95 per cent of all hydrogen produced. In electrolysis, water is split into oxygen and hydrogen through a process called electrolysis.
- Electrolytic processes take place in an electrolyser, which functions more like a fuel cell in reverse — instead of using the energy of a hydrogen molecule as a fuel cell does, an electrolyser creates hydrogen by splitting water molecules.
How hydrogen fuel cells work:
- Hydrogen fuel must therefore be transformed into electricity by a device called a fuel cell stack before it can be used to power a car or truck. A fuel cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy using oxidising agents through an oxidation-reduction reaction. Fuel cell-based vehicles most commonly combine hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity to power the electric motor on board.
Benefits of using hydrogen fuel cell:
- Hydrogen fuel cell cars have a near-zero carbon footprint. Hydrogen is about 2-3 times as efficient as burning petrol, because an electric chemical reaction is much more efficient than combustion.
- The new HFC technology bus prototype unveiled in Pune used a fuel cell which is known as, “low temperature proton exchange membrane type fuel cell”, that operates at 65-75°C, which is suitable for vehicular applications. These cells operate at relatively low temperatures and are the best candidates for powering automobiles.
Issues regarding use of hydrogen:
- Lack of fuelling station infrastructure
- Safety issues as hydrogen is stored in a pressurized cryogenic tank.
- Scaling up the technology
News 12: United States Agency for International Development:
- USAID leads international development and humanitarian efforts to save lives, reduce poverty, strengthen democratic governance and help people progress beyond assistance.
- It is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance.
India and USAID
- USAID has partnered with India to alleviate food insecurity, fuel the Green Revolution; eradicate polio and strengthen health systems; promote biodiversity and preserve India’s food crops; develop industry and infrastructure; establish leading research universities; develop its economy; and reduce poverty.
- The US Agency for International Development (USAID) and India’s Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) officially launched Forest-PLUS 2.0 on September 25, 2019.
- It is a five-year programme initiated in December 2018 that focuses on developing tools and techniques to bolster ecosystem management and harnessing ecosystem services in forest landscape management.
- The programme’s first set focused on capacity building to help India participate in Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation (REDD+). It included four pilot projects in Sikkim, Rampur, Shivamogga and Hoshangabad.
About REDD+:
- It means “Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation”, conservation of forest carbon stocks, sustainable management of forests, and enhancement of forest carbon stocks in developing countries.
- REDD+ is a mechanism developed by Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
News 13: M.P. first to draft suicide prevention strategy:
Understanding the sociological factors, suggesting preventive methods, devising ways to raise mass awareness and suggesting newer methods for the training of professionals and individuals. The committee will also look at how the laws can be strengthened or diluted to improve the situation and understand the inter-sectoral linkages in suicide prevention.
According to the National Crime Records Bureau’s Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India 2020, a total of 1,53,052 suicides were reported in the country with 14,578 reported from Madhya Pradesh, the third highest in the country.
News 14: Enforcement Directorate:
- Established: 1956
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- Ministry: Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance
- Objective: The Directorate of Enforcement is a multi-disciplinary organization mandated with investigation of the offence of money laundering and violations of foreign exchange laws.
- Functions of Enforcement Directorate:
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA): It is a criminal law enacted to prevent money laundering and to provide for confiscation of property derived from, or involved in, money-laundering and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA): It is a civil law enacted to consolidate and amend the laws relating to facilitate external trade and payments and to promote the orderly development and maintenance of foreign exchange market in India. ED has been given the responsibility to conduct investigation into suspected contraventions of foreign exchange laws and regulations, to adjudicate and impose penalties on those adjudged to have contravened the law.
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA): This law was enacted to deter economic offenders from evading the process of Indian law by remaining outside the jurisdiction of Indian courts. It is a law whereby the Directorate is mandated to attach the properties of the fugitive economic offenders who have escaped from India warranting arrest and provide for the confiscation of their properties to the Central Government.
News 15: Snake boat race on Pampa

News 16: Red panda



