Seismic activity has gone through the roof in last two months and the pacific ring of fire :-
Background :-
An earthquake estimated to be of magnitude 5.7 struck Ambassa in Tripura on 2nd Dec 2016 and tremors were felt in east and northeast India as well as in Bangladesh and Myanmar. High seismicity seen in the north and northeastern parts of the subcontinent is caused by the movement of the Indian continental plate into the Eurasian plate in the North at the rate of about 40-500 mm/year. The Himalayas are a product of this movement. The entire region extending from Afghanistan in the west to Myanmar in the east is known for its high seismicity.
Over the past 12 months, there have been 77 earthquakes in the region with a magnitude of over 4.0. Of these, three registered magnitudes of over 6.5 on the Richter’s scale—two of which had epicentres in Myanmar and one near Imphal in Manipur, respectively.
The earthquake is a part of increased seismic activity that has been observed over the past two months or so. Since December 2, 2016, there have been around 420 earthquakes of magnitude over 5 along all major continental plate boundaries. The average number of earthquakes above magnitude 5 per month is close to only 120. The seismic activity over December and the beginning of January, thus marks a 3.5-fold increase.
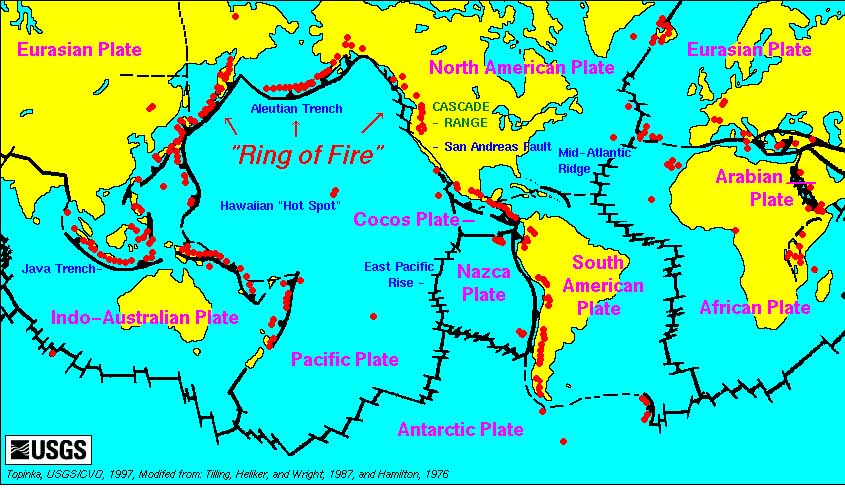
Apart from region of highest seismic activity—“the ring of fire” formed on the fringes of the Pacific plate—medium and strong earthquakes have been reported from the Eurasian plate, the Filipino plate, Australian plate, North American plate, the Caribbean plate, South American plate, the Arabian plate and the Indian plate. It is not yet clear whether these events are linked in anyway.
Indian Science Congress: chronic underfunding in this sector highlighted
The 104th session of the Indian Science Congress was inaugurated by Prime Minister recently at Tirupati. The theme of meeting this year is Science and Technology for National Development. In his speech, the PM talked about the importance of scientists to respond to change. He said that a deep-rooted curiosity-driven scientific tradition will allow quick adaptation to new realities.
He identified clean water, energy, food, environment, climate, security and healthcare as the important challenges that India faces.General President of the Indian Science Congress Association, D Narayana Rao, talked about how science and technology holds the promise to transform India.
He also highlighted chronic underfunding and understaffing in this sector and stated that it was important to redefine the role of science in national development in the time of globalisation. He said that technological independence is needed along with political independence.
Union Minister for Science & Technology & Earth Sciences, Harsh Vardhan, said that drastic changes in our thinking are needed to bring about fundamental changes.
Informative video on Health Report 2016 and Climate Change Report 2016
Savitribai Phule (Wife of Jyotiba Phule – the social reformer from Maharastra)- 19th Century Pioneer Still Inspires Many

Few details:
- Phule is widely regarded as one of India’s first generation modern feminists for her significant contributions in ensuring equal education opportunities under the British raj.
- She became the first female teacher in India in 1848 and opened a school for girls along with her husband, social reformer Jyotirao Phule. The two also worked against discrimination based on caste-based identity, something vehemently opposed by the orthodox sections of society in Pune.
- She went on to establish a shelter for widows in 1854 which she further built on in 1864 to also accommodate destitute women and child brides cast aside by their families.
- Phule also played a pivotal role in directing the work of the Satyashodhak Samaj, formed by her husband with the objective to achieve equal rights for the marginalised lower castes. She took over the reins of the organisation after Jyotirao’s death in 1890.
- Savitribai opened a clinic in 1897 for victims of the bubonic plague that spread across Maharashtra just before the turn of the century.
- In her honour, University of Pune was renamed Savitribai Phule University in 2014.

Recent Posts
The United Nations has shaped so much of global co-operation and regulation that we wouldn’t recognise our world today without the UN’s pervasive role in it. So many small details of our lives – such as postage and copyright laws – are subject to international co-operation nurtured by the UN.
In its 75th year, however, the UN is in a difficult moment as the world faces climate crisis, a global pandemic, great power competition, trade wars, economic depression and a wider breakdown in international co-operation.

Still, the UN has faced tough times before – over many decades during the Cold War, the Security Council was crippled by deep tensions between the US and the Soviet Union. The UN is not as sidelined or divided today as it was then. However, as the relationship between China and the US sours, the achievements of global co-operation are being eroded.
The way in which people speak about the UN often implies a level of coherence and bureaucratic independence that the UN rarely possesses. A failure of the UN is normally better understood as a failure of international co-operation.
We see this recently in the UN’s inability to deal with crises from the ethnic cleansing of the Rohingya Muslims in Myanmar, to civil conflict in Syria, and the failure of the Security Council to adopt a COVID-19 resolution calling for ceasefires in conflict zones and a co-operative international response to the pandemic.
The UN administration is not primarily to blame for these failures; rather, the problem is the great powers – in the case of COVID-19, China and the US – refusing to co-operate.
Where states fail to agree, the UN is powerless to act.
Marking the 75th anniversary of the official formation of the UN, when 50 founding nations signed the UN Charter on June 26, 1945, we look at some of its key triumphs and resounding failures.
Five successes
1. Peacekeeping
The United Nations was created with the goal of being a collective security organisation. The UN Charter establishes that the use of force is only lawful either in self-defence or if authorised by the UN Security Council. The Security Council’s five permanent members, being China, US, UK, Russia and France, can veto any such resolution.
The UN’s consistent role in seeking to manage conflict is one of its greatest successes.
A key component of this role is peacekeeping. The UN under its second secretary-general, the Swedish statesman Dag Hammarskjöld – who was posthumously awarded the Nobel Peace prize after he died in a suspicious plane crash – created the concept of peacekeeping. Hammarskjöld was responding to the 1956 Suez Crisis, in which the US opposed the invasion of Egypt by its allies Israel, France and the UK.
UN peacekeeping missions involve the use of impartial and armed UN forces, drawn from member states, to stabilise fragile situations. “The essence of peacekeeping is the use of soldiers as a catalyst for peace rather than as the instruments of war,” said then UN Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar, when the forces won the 1988 Nobel Peace Prize following missions in conflict zones in the Middle East, Africa, Asia, Central America and Europe.
However, peacekeeping also counts among the UN’s major failures.
2. Law of the Sea
Negotiated between 1973 and 1982, the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) set up the current international law of the seas. It defines states’ rights and creates concepts such as exclusive economic zones, as well as procedures for the settling of disputes, new arrangements for governing deep sea bed mining, and importantly, new provisions for the protection of marine resources and ocean conservation.
Mostly, countries have abided by the convention. There are various disputes that China has over the East and South China Seas which present a conflict between power and law, in that although UNCLOS creates mechanisms for resolving disputes, a powerful state isn’t necessarily going to submit to those mechanisms.
Secondly, on the conservation front, although UNCLOS is a huge step forward, it has failed to adequately protect oceans that are outside any state’s control. Ocean ecosystems have been dramatically transformed through overfishing. This is an ecological catastrophe that UNCLOS has slowed, but failed to address comprehensively.
3. Decolonisation
The idea of racial equality and of a people’s right to self-determination was discussed in the wake of World War I and rejected. After World War II, however, those principles were endorsed within the UN system, and the Trusteeship Council, which monitored the process of decolonisation, was one of the initial bodies of the UN.
Although many national independence movements only won liberation through bloody conflicts, the UN has overseen a process of decolonisation that has transformed international politics. In 1945, around one third of the world’s population lived under colonial rule. Today, there are less than 2 million people living in colonies.
When it comes to the world’s First Nations, however, the UN generally has done little to address their concerns, aside from the non-binding UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples of 2007.
4. Human rights
The Human Rights Declaration of 1948 for the first time set out fundamental human rights to be universally protected, recognising that the “inherent dignity and of the equal and inalienable rights of all members of the human family is the foundation of freedom, justice and peace in the world”.
Since 1948, 10 human rights treaties have been adopted – including conventions on the rights of children and migrant workers, and against torture and discrimination based on gender and race – each monitored by its own committee of independent experts.
The language of human rights has created a new framework for thinking about the relationship between the individual, the state and the international system. Although some people would prefer that political movements focus on ‘liberation’ rather than ‘rights’, the idea of human rights has made the individual person a focus of national and international attention.
5. Free trade
Depending on your politics, you might view the World Trade Organisation as a huge success, or a huge failure.
The WTO creates a near-binding system of international trade law with a clear and efficient dispute resolution process.
The majority Australian consensus is that the WTO is a success because it has been good for Australian famers especially, through its winding back of subsidies and tariffs.
However, the WTO enabled an era of globalisation which is now politically controversial.
Recently, the US has sought to disrupt the system. In addition to the trade war with China, the Trump Administration has also refused to appoint tribunal members to the WTO’s Appellate Body, so it has crippled the dispute resolution process. Of course, the Trump Administration is not the first to take issue with China’s trade strategies, which include subsidises for ‘State Owned Enterprises’ and demands that foreign firms transfer intellectual property in exchange for market access.
The existence of the UN has created a forum where nations can discuss new problems, and climate change is one of them. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was set up in 1988 to assess climate science and provide policymakers with assessments and options. In 1992, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change created a permanent forum for negotiations.
However, despite an international scientific body in the IPCC, and 165 signatory nations to the climate treaty, global greenhouse gas emissions have continued to increase.
Under the Paris Agreement, even if every country meets its greenhouse gas emission targets we are still on track for ‘dangerous warming’. Yet, no major country is even on track to meet its targets; while emissions will probably decline this year as a result of COVID-19, atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases will still increase.
This illustrates a core conundrum of the UN in that it opens the possibility of global cooperation, but is unable to constrain states from pursuing their narrowly conceived self-interests. Deep co-operation remains challenging.
Five failures of the UN
1. Peacekeeping
During the Bosnian War, Dutch peacekeeping forces stationed in the town of Srebrenica, declared a ‘safe area’ by the UN in 1993, failed in 1995 to stop the massacre of more than 8000 Muslim men and boys by Bosnian Serb forces. This is one of the most widely discussed examples of the failures of international peacekeeping operations.
On the massacre’s 10th anniversary, then UN Secretary General Kofi Annan wrote that the UN had “made serious errors of judgement, rooted in a philosophy of impartiality”, contributing to a mass murder that would “haunt our history forever”.
If you look at some of the other infamous failures of peacekeeping missions – in places such as Rwanda, Somalia and Angola – it is the limited powers given to peacekeeping operations that have resulted in those failures.
2. The invasion of Iraq
The invasion of Iraq by the US in 2003, which was unlawful and without Security Council authorisation, reflects the fact that the UN is has very limited capacity to constrain the actions of great powers.
The Security Council designers created the veto power so that any of the five permanent members could reject a Council resolution, so in that way it is programmed to fail when a great power really wants to do something that the international community generally condemns.
In the case of the Iraq invasion, the US didn’t veto a resolution, but rather sought authorisation that it did not get. The UN, if you go by the idea of collective security, should have responded by defending Iraq against this unlawful use of force.
The invasion proved a humanitarian disaster with the loss of more than 400,000 lives, and many believe that it led to the emergence of the terrorist Islamic State.
3. Refugee crises
The UN brokered the 1951 Refugee Convention to address the plight of people displaced in Europe due to World War II; years later, the 1967 Protocol removed time and geographical restrictions so that the Convention can now apply universally (although many countries in Asia have refused to sign it, owing in part to its Eurocentric origins).
Despite these treaties, and the work of the UN High Commission for Refugees, there is somewhere between 30 and 40 million refugees, many of them, such as many Palestinians, living for decades outside their homelands. This is in addition to more than 40 million people displaced within their own countries.
While for a long time refugee numbers were reducing, in recent years, particularly driven by the Syrian conflict, there have been increases in the number of people being displaced.
During the COVID-19 crisis, boatloads of Rohingya refugees were turned away by port after port. This tragedy has echoes of pre-World War II when ships of Jewish refugees fleeing Nazi Germany were refused entry by multiple countries.
And as a catastrophe of a different kind looms, there is no international framework in place for responding to people who will be displaced by rising seas and other effects of climate change.
4. Conflicts without end
Across the world, there is a shopping list of unresolved civil conflicts and disputed territories.
Palestine and Kashmir are two of the longest-running failures of the UN to resolve disputed lands. More recent, ongoing conflicts include the civil wars in Syria and Yemen.
The common denominator of unresolved conflicts is either division among the great powers, or a lack of international interest due to the geopolitical stakes not being sufficiently high. For instance, the inaction during the Rwandan civil war in the 1990s was not due to a division among great powers, but rather a lack of political will to engage.
In Syria, by contrast, Russia and the US have opposing interests and back opposing sides: Russia backs the government of the Syrian dictator Bashar al-Assad, whereas the US does not.
5. Acting like it’s 1945
The UN is increasingly out of step with the reality of geopolitics today.
The permanent members of the Security Council reflect the division of power internationally at the end of World War II. The continuing exclusion of Germany, Japan, and rising powers such as India and Indonesia, reflects the failure to reflect the changing balance of power.
Also, bodies such as the IMF and the World Bank, which are part of the UN system, continue to be dominated by the West. In response, China has created potential rival institutions such as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank.
Western domination of UN institutions undermines their credibility. However, a more fundamental problem is that institutions designed in 1945 are a poor fit with the systemic global challenges – of which climate change is foremost – that we face today.


